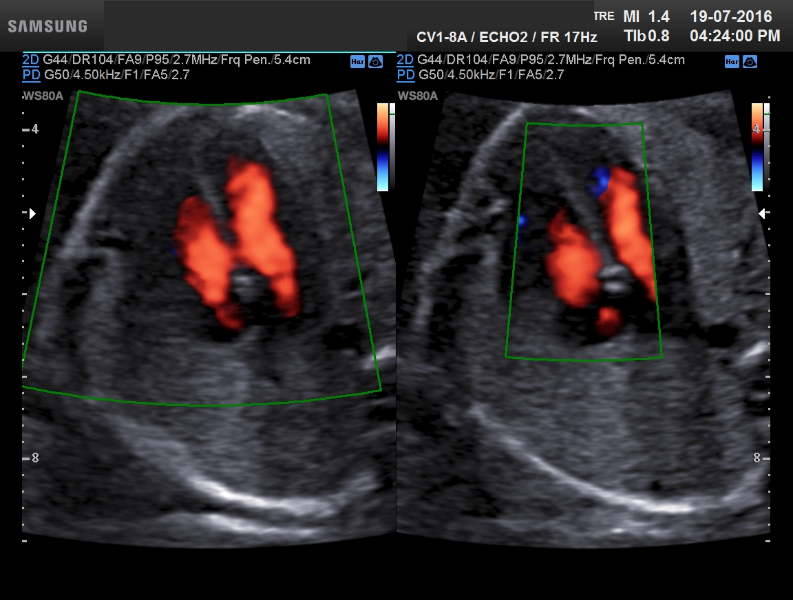
Echocardiogram
Echocardiogram in children (“echo”) is an ultrasound test that uses sound waves to view the heart. It is safe, painless, and without radiation. Pictures of the child’s heart can be viewed on a small monitor while the procedure is being performed. The echocardiogram focuses specifically on the heart and blood vessels around the heart. It is used to diagnose or exclude congenital or acquired heart problems. Assessment of heart function can be made with an echocardiogram
Fetal echocardiography
Fetal echocardiography is a test similar to an ultrasound. This exam allows your doctor to better see the structure and function of your unborn child’s heart. It’s typically done in the second trimester between 18 to 20 weeks. The exam uses sound waves that “echo” off the structures of the fetus’s heart. A machine analyses these sound waves and creates a picture, or echocardiogram, of their heart’s interior. This image provides information on how your baby’s heart formed and whether it’s working properly.
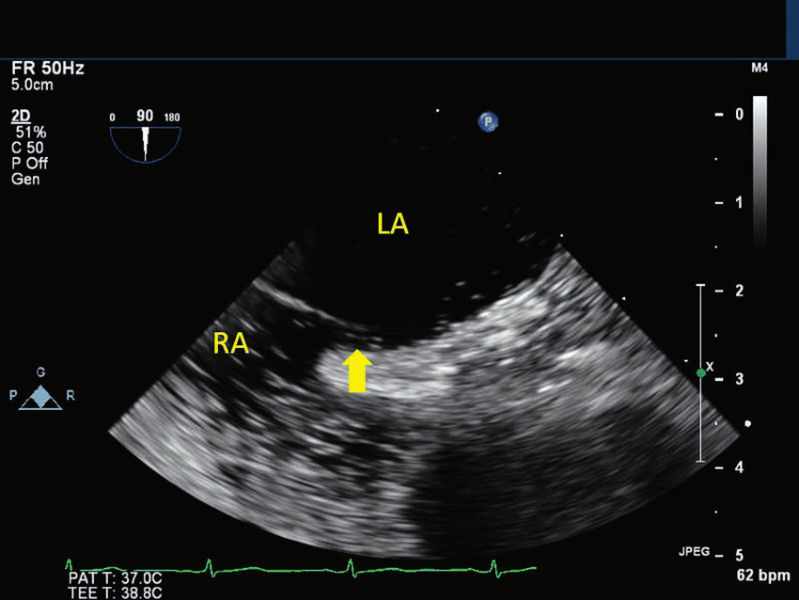
Transesophageal Echocardiogram
A transesophageal echo (TEE) test is a type of echo that uses a long, thin, tube (endoscope) to guide the ultrasound transducer down the oesophagus (“food pipe” that goes from the mouth to the stomach). This lets the doctor see pictures of the heart without the ribs or lungs getting in the way. A TEE is done when your doctor needs a closer look at your heart or does not get the information needed from a regular echo.
Paediatric cardiac catheterisation
Cardiac catheterization is a procedure that involves puncturing an artery and / or vein, usually located in the groin, so that a small, long, flexible tube (catheter) can be guided into the heart and major vessels around the heart. The catheter is moved through the heart with the aid of fluoroscopy in the catheterisation laboratory. This is usually performed to help in providing a diagnosis of heart problems.

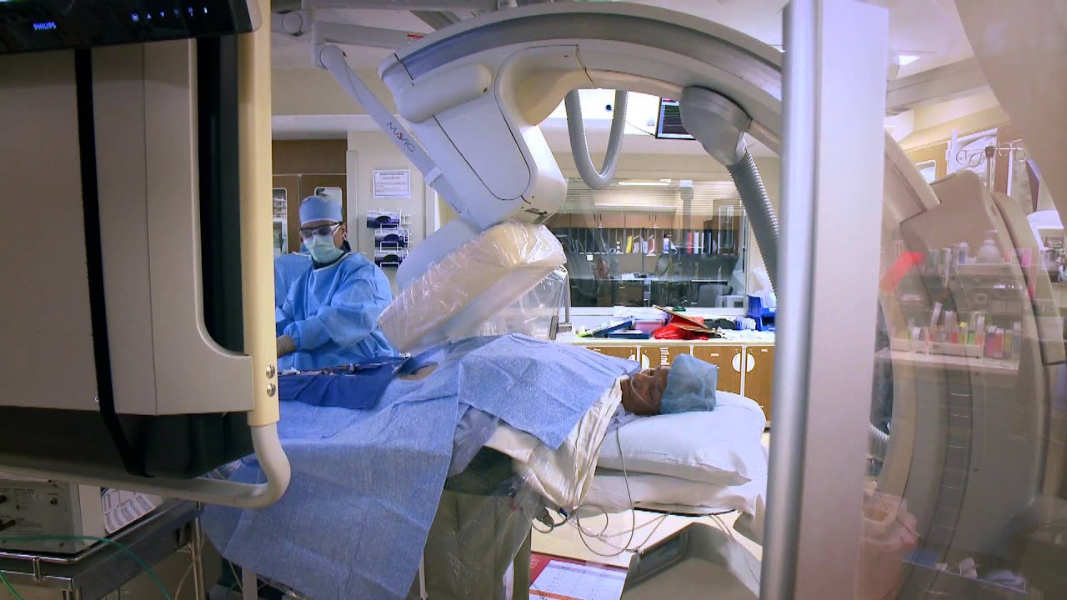
Interventional cardiac catheterization
Interventional cardiac catheterization is a type of cardiac catheterization where actual treatments can be performed by use of specialized catheters. These specialized catheters include balloon catheters that can open up narrowed valves or arteries and also catheters where devices can be deployed which can close extra vessels or certain “holes” in the heart.
Preoperative Cardiac Evaluation
Preoperative assessment of paediatric patients with congenital heart disease is essential to optimal intraoperative and postoperative management. Congenital heart defects can be complex. The preoperative data should be carefully collected, appropriately organized, and synthesized based on the underlying physiologic problems. Clinical assessment should focus on identifying factors that can be modified to optimize a patient’s preoperative clinical status as well as those that could potentially affect the intraoperative and postoperative courses.


Post operative cardiac care in children
Postoperative care of cardiac patients requires a comprehensive and multidisciplinary approach to critically ill patients with cardiac disease whose care requires a clear understanding of cardiovascular physiology, multi organ system function, and organ interactions in health and in disease.